Environmental Test Chambers for Thermal Shock Testing
Thermal shock testing simulates the extreme temperature changes a product might be exposed to during real-life use in customers' hands. For example, think of the jolt a smartphone battery experiences when somebody moves from cold winter conditions outside to the heated space of a home.
Or the contrast in temperatures airplane parts must endure, departing an airport runway in 95-degree weather and encountering -40°F to -70°F when reaching peak altitude.
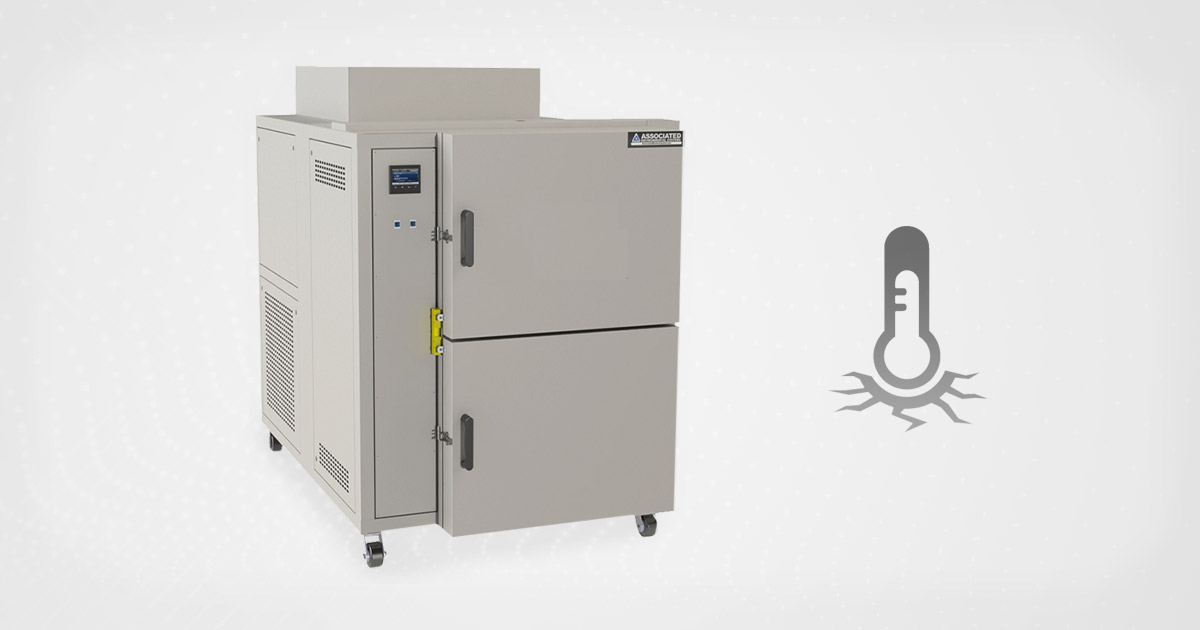
Thermal shock chambers apply alternating extreme hot and cold air to products to test their durability and identify breaking points. This method reduces the potential for failures. These chambers feature two zones: heat and cold, with an optional third zone for ambient temperature.
Associated Environmental Systems (AES) manufactures industry-leading thermal shock chambers to empower businesses that need to guarantee their products can withstand rapid temperature changes. Used often for the testing of electronic components in the automotive, packaging and defense industries, the SM Series test chambers have led to innovations and delivered peace of mind for companies and consumers alike.
What is the Price of a Thermal Shock Chamber

The price of a thermal shock chamber can vary significantly, often starting around $100,000. Several factors influence the final cost, including chamber size, performance capabilities, and custom features. For example, larger chambers or those with advanced capabilities generally command a higher price due to the added complexity and materials involved.
Customizations such as extended temperature ranges, specialized materials, or automation features can increase the base price. When selecting a thermal shock chamber, working closely with a manufacturer ensures that you receive the right model to meet your specific testing requirements.
Industries That Rely on Thermal Shock Chambers
Thermal shock chambers are essential tools for evaluating the resilience and reliability of products subjected to rapid and extreme temperature changes across a range of demanding industries. These specialized environmental test chambers rapidly cycle products between hot and cold temperature zones, inducing thermal stress that can reveal critical weaknesses and potential failure points.
Explore how thermal shock testing plays a role in each industry:
-
Semiconductor: Replicating extreme thermal transitions to ensure the reliability of integrated circuits
-
Energy Storage: Evaluates how rapid temperature shifts affect the efficiency and lifespan of energy storage solutions.
-
Consumer Products: Simulating the thermal stresses everyday products may encounter to ensure longevity.
-
Military & Defense: Providing thermal shock testing to meet the demanding environmental standards of MIL-STDs.
-
Consumer Electronics: Assessing the impact of sudden temperature changes on the functionality and lifespan of electronic devices.
Want to learn more about how we support each industry? Explore the industries we serve to see how our solutions align with your specific needs.
AES THERMAL SHOCK CHAMBERS
AES offers the:
SM Series
The SM Floor series floor model thermal shock features two zones. Your product sits in a pneumatically controlled basket that travels vertically between the two zones within seconds.
Hot Zone: Above Ambient* to +200°C (Above Ambient* to +392°F)
Cold Zone: -65°C to +121°C(-85°F to +250°F)
Thermal Shock Construction
The exterior chamber construction includes a powder-coat finish over heavy-gauge steel and type 304 stainless steel on the inside. Sandwiched between is a layer of highly-efficient, low K-factor, thermal insulation for the highest efficiency and temperature performance.
The SM Series features two zones. To achieve the rapid change in temperature, your product sits in a pneumatically controlled basket that travels vertically between the two zones within seconds. (An optional third zone for ambient temperature can be added; see below the video).
Each compartment holds your desired temperature with a heated zone and a cold zone. The specially designed basket is a traveling workspace with its own sensor so you can monitor the environmental condition in each zone, the temperature of the specimen, and its recovery time.
When you need to cool your specimen even faster, an optional liquid LN2 or CO2 boost can be added.
A third zone can be joined between the hot and cold for ambient temperature exposure.
Cooling differences between 2900 models and 9100 models should be noted.
- 2100 models are cooled with a cascade mechanical refrigeration system. An LN2 boost option can be added to cool even faster.
- 1900 models use liquid nitrogen to reach cold temperatures. There is no mechanical refrigeration.
Heating & Cooling Zone
Heating Zone
AES heating systems are all-electric. They work by passing air over fast-response, low-watt-density resistance heaters with a ceramic core, ensuring a long reliable life with no downtime.
The combination of airflow, instrument response, and these fast-reacting heaters give highly accurate and straight-line control of temperatures. AES’s heating systems support temperatures upwards of 180°C (356°F), and heaters may be controlled independently or in unison.
Heating systems are located in a plenum so that test items are not subject to direct radiation.
Cooling Zone
Thermal shock chambers with fast change rates are designed to get you testing as soon as possible. The SM Series has an average pull-down rate of 2.5°C/ minute and an average ramp rate of 4.4°C/ minute.
The chambers feature liquid cooling. This power-efficient method takes up a smaller area than air-cooled options. Keep in mind that liquid-cooled chambers require a water supply.
You can reach temperatures as low as -70ºC with a standard SM Series chamber, although there are ways to go even colder.
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) and carbon dioxide (C02) boost options are available. While CO2 has a boiling point of -57°C (-70.6°F) and can be stored in smaller amounts, LN2 has a boiling point of -196°C (-320.8°F). Therefore, liquid nitrogen provides pull-down rates that are much faster.
Remote Monitoring With AESONE CONNECT®
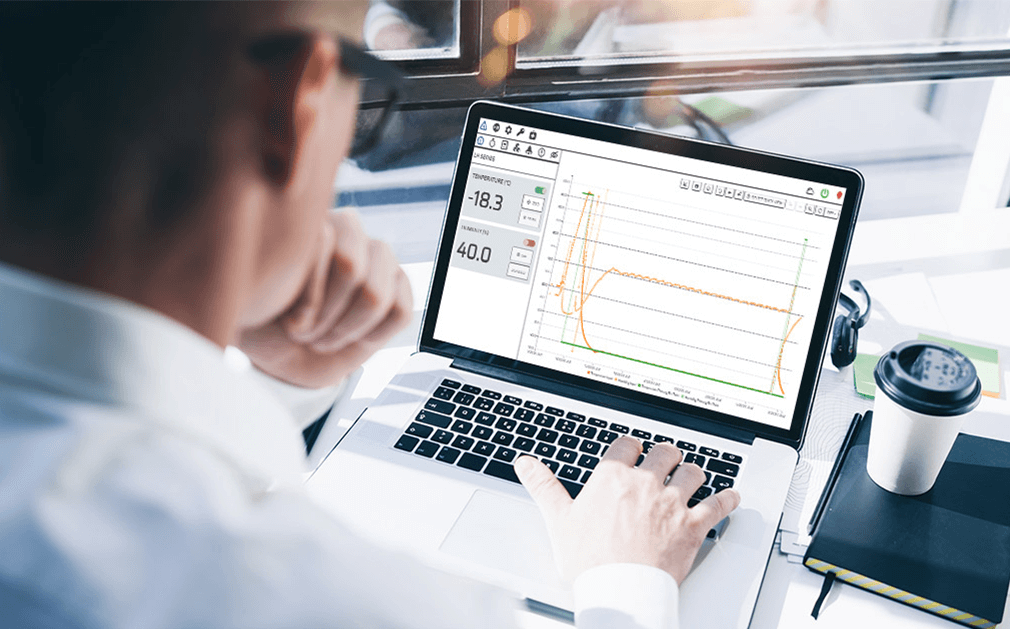
chambers come standard with AESONE CONNECT®, a combination of hardware and software solutions that enables you to monitor tests remotely. You can view real-time and historical data, create, edit, save, start, stop and move between test profiles from anywhere you can access a web browser.
Watching from a full-screen monitor, AESONE CONNECT® empowers you to design and rearrange tests with visually intuitive plot lines, clear data intervals, and colorful graphs. Furthermore, sharing a chamber is not a security problem. The administrator controls multiple login authentication methods and user-access permission levels and can establish expiration dates for each user.
If your budget can’t afford to purchase a new temperature and humidity chamber, AESONE technology can also be retrofitted to nearly any chamber you own. An AES team member will examine your configuration and retrofit the AESONE CONNECT® hardware to your chamber so you can connect to the dashboard.
Notably, well-cared-for chambers can function longer than ten years, outlasting their controller technology. Retrofits enable you to extend the lifespan of your chamber even further.
Ready to get started?
Reach out now by phone, chat, or form submission. Our team is ready to help you!